Overview
We provide the ability for you to search your data in a fast and performant manner. We have multiple search paradigms, which are exposed through the search over chunks route, the search within groups route, and the search over groups route.
query: The user query that is embedded and searched against the dataset.search_type: Can be semantic, fulltext, or hybrid.
Semantic: Uses cosine distance to determine the most relevant results.
Fulltext: Uses a SPLADE model to find the most relevant results.
Hybrid: Uses a reranker model that pulls one page of results from both fulltext and semantic searches to find the most relevant results.page: The page of chunks to fetch. Pages are 1-indexed.page_size: This lets you tune the number of results that are returned.highlight_results: Enables subsentence highlighting of relevant portions of the text.slim_chunks: Excludes chunk_html from the returned results to reduce network bandwidth. Useful for large chunks.recency_bias: A value from 0-1 that tunes how much the recency of chunks (based on the timestamp field) affects the ranking.sort_options: Options on how to sort.filters: Apply filters to get exactly the results you want.
Search Modes
Trieve offers 4 different types of search.
Semantic Search
Semantic search uses an embeddnig model to generate a query vector. Defaults to using cosine similarity and jina-base-en
Trieve uses only the embedding model to select and rerank the results.
This search_type is semantic.
Full Text search
FullText search uses a SPLADE model to find the most relevant results to your given query.
This search_type is fulltext.
BM25
BM25 is the classical type of search index, it uses the BM25 ranking function to determine the results that are most similar to your given query.
This search_type is bm25.
Hybrid
Hybrid search, does both a full text search, and semantic search. From those results it then uses a reranker model ( defaults to bge-reranker-large).
This search_type is hybrid.
Search Paradigms
We offer three different search strategies for you to choose from:
- Search over chunks: This strategy allows you to search all of your chunks independently. This is useful when your chunks are independent and do not need to be grouped together.
- Search within groups: This strategy lets you constrain your results to within a selected group. This is useful for searching distinct groups within your dataset independently.
- Search over groups: This strategy allows you to search over the groups of chunks within your dataset. This returns the groups and the top chunks within each group that matched your query, providing better search quality for datasets with highly related chunks within groups.
Search over chunks
POST /api/chunk/search
Headers:
{
"TR-Dataset": "<your-dataset-id>",
"Authorization": "tr-*******************"
}
Body:
{
"query": "How to search with Trieve",
"search_type": "fulltext",
"page": 1,
"page_size": 10,
"score_threshold": 0.5
}
Search within group
POST /api/chunk_group/search
Headers:
{
"TR-Dataset": "<your-dataset-id>",
"Authorization": "tr-*******************"
}
Body:
{
"group_tracking_id": "my-group-tracking-id",
"query": "How to search with Trieve",
"search_type": "fulltext",
"page": 1,
"page_size": 10,
"score_threshold": 0.5
}
Search over groups
POST api/chunk_group/group_oriented_search
Headers:
{
"TR-Dataset": "<your-dataset-id>",
"Authorization": "tr-*******************"
}
Body:
{
"group_tracking_id": "my-group-tracking-id",
"group_size": 5,
"query": "How to search with Trieve",
"search_type": "fulltext",
"page": 1,
"page_size": 10,
"score_threshold": 0.5
}
You can use the search UI at search.trieve.ai to A/B test which search method works best for you. Filters
Trieve filters are structured around three clauses:
must: All filters within this clause must be matched to return the chunks.must_not: All filters in this clause must not be matched to return the chunks.should: Any of these conditions can be matched to return a chunk.
Each clause contains a field_condition.
range: Match a number between a range of lt, gt, lte or gtematch_all: A list, every field must have have a match.match_any: A list, at least 1 field must be present.date_range: Match a date between a range of lt, gt, lte or gtegeo_radius: Match a radius based on a center and a radiusboolean: Matches if the field is true or false
Get chunks with both “CO” and “321” in their tag_set
"filters": {
"must": [
{
"field": "tag_set",
"match_all": ["CO", "321"]
}
]
}
Get chunks with either “CO” OR “321” in their tag_set:
"filters": {
"must": [
{
"field": "tag_set",
"match_any": ["CO", "321"]
}
]
}
Get chunks that are tagged within a GEO radius
"filters": {
"must": [
{
"field": "geo_radius",
"geo_radius": {
"center": {
"lat": 20,
"long": -30
},
"radius": 20,
}
}
]
}
Get chunks with neither “CO” nor “321” in their tag_set:
"filters": {
"must_not": [
{
"field": "tag_set",
"match_all": ["CO", "321"]
}
]
}
Get chunks that either don’t have “CO” in their tag_set or don’t have “321” in their tag_set:
"filters": {
"must_not": [
{
"field": "tag_set",
"match_any": ["CO", "321"]
},
]
}
Get chunks that either have “CO” in their tag_set or “http://example.com” in their link:
"filters": {
"should": [
{
"field": "tag_set",
"match": ["CO"]
},
{
"field": "link",
"match": ["http://example.com"]
}
]
}
Get Chunks that have num_value between 20 and 30
"filters": {
"must": [
{
"field": "num_value",
"range": {
"gte": 20.0,
"lte": 30.0,
"gt": 30.0,
"lt": 20.0
}
}
]
}
Rerank By
rerank_type can be either
fulltext: This will use the fulltext index to rerank the results, if search_type is fulltext then nothing different will happen.cross_encoder: This will use the Reranker model that you predefined. By default hybrid search will use the cross_encoder.bm25: This will use the bm25 matching algorithm rerank the results, if search_type is bm25 then nothing different will happen.semantic: This will use the semantic vectors to rerank the results, if search_type is semantic then nothing different will happen.
{
"sort_options": {
"sort_by" {
"rerank_type": "fulltext"
}
}
}
Multi Query
MultiQuery provides a way to give multiple query objects with a given weight bias.
To use the multiquery, instead of a single string, the query parameter receives a list of tuples,
value 1 being the query and value 2 being a value on how important it is.
As an example, search
Searching, but the search term of “iphone” and a color.
"query": [
[ "Flagship", 2 ],
[ "Red", 2 ],
[ "Iphone mini", 10 ]
]
Customizing your search models
Trieve offers many ways to customize your embedding models and reranker models. Different embedding models and different reranker models are better suited for different tasks.
Embedding Models
Trieve supports multiple embedding models that can be used to search over your data.
You can specify the embedding model to use in the server_configuration field when creating a dataset.
After creating a dataset, you cannot change the embedding model. If you need to change the embedding model, you must create a new dataset.
Reranker models
Trieve supports multiple reranker models that can be used to rerank the search results.
Currently, Trieve supports the BAAI bge-reranker-large model, AIMon’s aimon-rerank model, and Cohere’s rerank-v3.5 model.
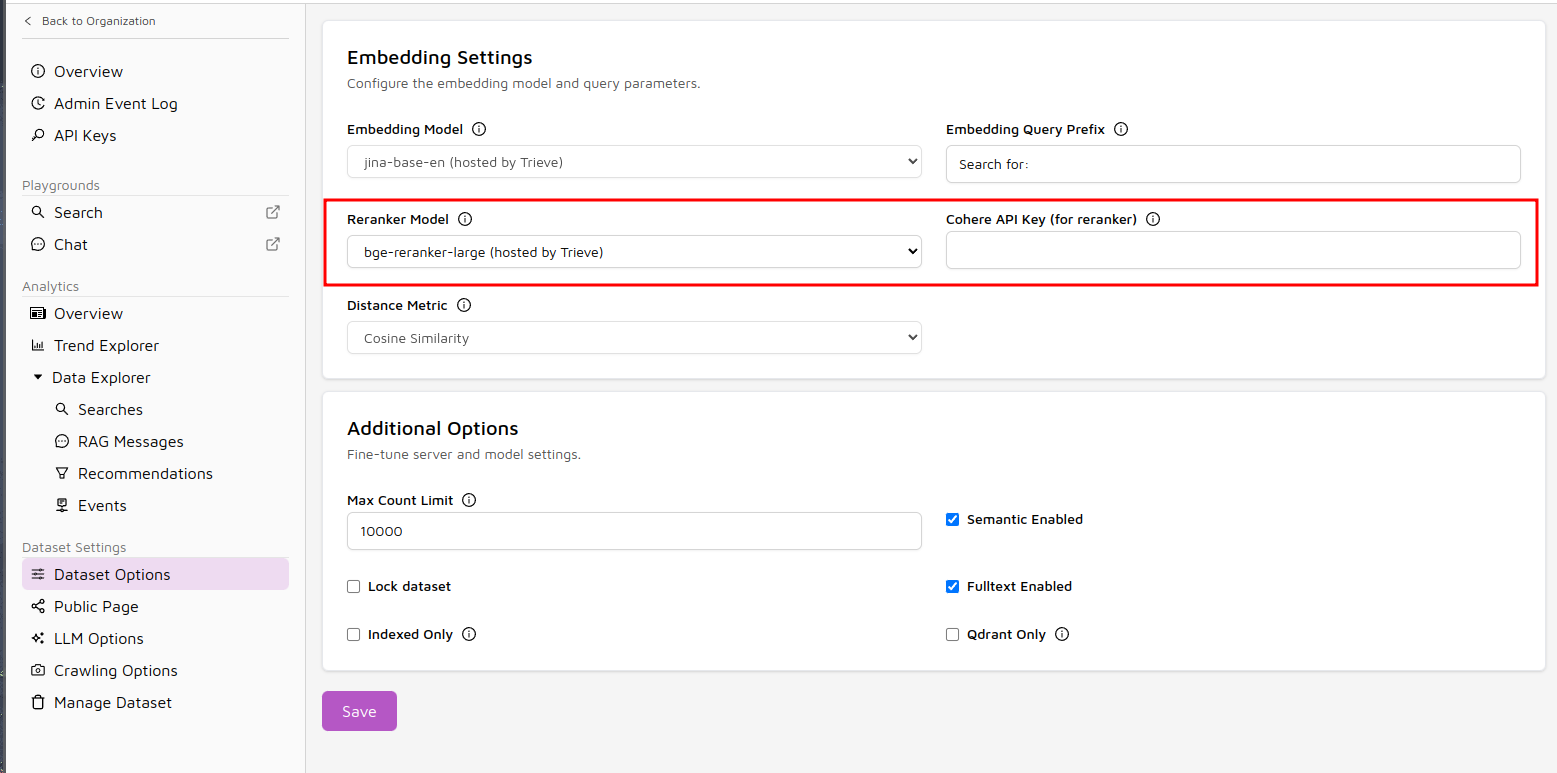
BAAI/bge-reranker-large
bge-reranker-large is a model by the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI) and is hosted by Trieve. This model does not require any additional configuration and will be used by default on all hybrid searches.
To manually select the bge-reranker-large as your reranker model, make a request to the update dataset route with the following parameters:
curl --request POST \
--url https://api.trieve.ai/api/dataset \
--header 'Authorization: <api-key>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'TR-Organization: <tr-organization>' \
--data '{
"dataset_name": "New Dataset", // Replace with a name for your dataset
"organization_id": "********-****-****-****-************",
// Update with the desired configurations for your dataset
"server_configuration": {
"RERANKER_MODEL_NAME":"bge-reranker-large"
}
}'
AIMon’s aimon-rerank
aimon-rerank is a model hosted by AIMon. To use this model, you must provide the aimon_api_key in the server_configuration field when creating a dataset.
To switch your reranker model to AIMon’s aimon-rerank, make a request to the update dataset route with the following parameters:
curl --request POST \
--url https://api.trieve.ai/api/dataset \
--header 'Authorization: <api-key>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'TR-Organization: <tr-organization>' \
--data '{
"dataset_name": "New Dataset", // Replace with a name for your dataset
"organization_id": "********-****-****-****-************",
// Update with the desired configurations for your dataset
"server_configuration": {
"RERANKER_BASE_URL":"https://pbe-api.aimon.ai/v1/rerank-icl",
"RERANKER_MODEL_NAME":"aimon-rerank",
"RERANKER_API_KEY":"<aimon_api_key>",
"AIMON_RERANKER_TASK_DEFINITION": "<a_task_definition>"
// A task definition can be used to specify the domain of the context documents for AIMon reranker.
// example of a task definition: "Your task is to grade the relevance of context document(s) in the domain of music and arts."
}
}'
Cohere’s rerank-v3.5
rerank-v3.5 is a model hosted by Cohere. To use this model, you must provide the cohere_api_key in the server_configuration field when creating a dataset.
To switch your reranker model to Cohere’s rerank-v3.5, make a request to the update dataset route with the following parameters:
curl --request POST \
--url https://api.trieve.ai/api/dataset \
--header 'Authorization: <api-key>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'TR-Organization: <tr-organization>' \
--data '{
"dataset_name": "New Dataset", // Replace with a name for your dataset
"organization_id": "********-****-****-****-************",
// Update with the desired configurations for your dataset
"server_configuration": {
"RERANKER_BASE_URL":"https://api.cohere.com/v2",
"RERANKER_MODEL_NAME":"rerank-v3.5"
"RERANKER_API_KEY":"<cohere_api_key>"
}
}'
