Installing Trieve on AWS (EKS)
Things you need
- Domain name
- An allowance for at least 8vCPU for G and VT instances
- helm cli
- aws cli
- kubectl
- k9s (optional)
Clone the Trieve repository
git clone https://github.com/devflowinc/trieve.git
cd trieve
Login to AWS
aws should be configured with your IAM credentails chosen. Run the following commands to create the EKS cluster
cd terraform/aws
terraform init
terraform apply
Login to the cluster
Set up your kubeconfig to point to the new cluster
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region us-east-2 --name trieve-aws-cluster
Install Ingress nginx + Cert Manager
Ingress-nginx + Cert manager is how we will expose the trieve services to the internet.
Feel free to use whatever ingress controller you are comfortable with.
# To install ingress-nginx
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.12.0-beta.0/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml
# To install cert-manager
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.16.2/cert-manager.yaml
# To install ClusterIssuer
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/devflowinc/trieve-helm/refs/heads/main/charts/trieve/test-production/cluster-issuer.yaml
Setup StorageClass
kubectl patch storageclass gp2 -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
Install Trieve
Download values.yaml file
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/devflowinc/trieve-helm/refs/heads/main/charts/trieve/values.yaml
Modify domain names for ingresses
Download values.yaml file
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/devflowinc/trieve-helm/refs/heads/main/charts/trieve/values.yaml
Modify domain names for ingresses
domains:
dashboard:
disabled: false
host: dashboard.yourdomain.com
class: nginx
# Annotations for the ingress
# Annotations for the service that the ingress points to
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
acme.cert-manager.io/http01-edit-in-place: "true"
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
tls:
- hosts:
- dashboard.yourdomain.com
secretName: dashboard-domain
serviceAnnotations: {}
server:
disabled: false
host: api.yourdomain.com
class: nginx
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
acme.cert-manager.io/http01-edit-in-place: "true"
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
tls:
- hosts:
- api.yourdomain.com
secretName: api-domain
serviceAnnotations: {}
search:
disabled: false
host: search.yourdomain.com
class: nginx
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
acme.cert-manager.io/http01-edit-in-place: "true"
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
tls:
- hosts:
- search.yourdomain.com
secretName: search-domain
serviceAnnotations: {}
chat:
disabled: false
host: chat.yourdomain.com
class: nginx
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
acme.cert-manager.io/http01-edit-in-place: "true"
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
tls:
- hosts:
- chat.yourdomain.com
secretName: chat-domain
serviceAnnotations: {}
## ...
config:
## For the frontend to communicate
vite:
apiHost: https://api.yourdomain.com/api
searchUiUrl: https://search.yourdomain.com
chatUiUrl: https://chat.yourdomain.com
dashboardUrl: https://dashboard.yourdomain.com
## For the backend oidc server
oidc:
issuerUrl: "https://auth.yourdomain.com/realms/trieve"
authRedirectUrl: "https://auth.yourdomain.com/realms/trieve/protocol/openid-connect/auth"
helm repo add trieve https://devflowinc.github.io/trieve-helm/
helm repo update
helm upgrade -i -f helm/values.yaml trieve-local trieve/trieve
helm upgrade -i -f helm/values.yaml trieve-local trieve/trieve
You will need to install the helm chart twice to ensure the crds are installed and ConfigMap’s are updated properly.
Verify the installation
After installing, kubectl get deployments should look like this.
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
bktree-worker 1/1 1 1 14m
chat 1/1 1 1 14m
crawl-worker 1/1 1 1 14m
dashboard 1/1 1 1 14m
delete-worker 1/1 1 1 14m
group-worker 1/1 1 1 14m
ingest 10/10 10 10 14m
keycloak-operator 1/1 1 1 46m
redis 1/1 1 1 46m
search 1/1 1 1 14m
server 3/3 1 0 14m
sync-qdrant 0/0 0 0 14m
word-worker 1/1 1 1 14m
Set Ingress
Get Ingress ip address
You will get an output like this:
ingress-chat nginx chat.yourdomain.com 4.157.193.10 80, 443 7m43s
ingress-dashboard nginx dashboard.yourdomain.com 4.157.193.10 80, 443 7m43s
ingress-keycloak nginx auth.yourdomain.com 4.157.193.10 80, 443 20m
ingress-search nginx search.yourdomain.com 4.157.193.10 80, 443 7m43s
ingress-server nginx api.yourdomain.com 4.157.193.10 80, 443 7m43s
Add A records
Add A records to your domain registrar with the IP address of the ingress.
chat.yourdomain.com -> 4.157.193.10 # Example IP
dashboard.yourdomain.com -> 4.157.193.10 # Example IP
search.yourdomain.com -> 4.157.193.10 # Example IP
api.yourdomain.com -> 4.157.193.10 # Example IP
helm upgrade -i -f values.yaml trieve-local trieve/trieve after making changes. to apply them.
Post Installation
Setup Keycloak redirect urls
- Navigate to auth.yourdomain.com
- Log in using the default credentials:
- Username: admin
- Password: password
- Switch the Realm from “master” to “trieve”
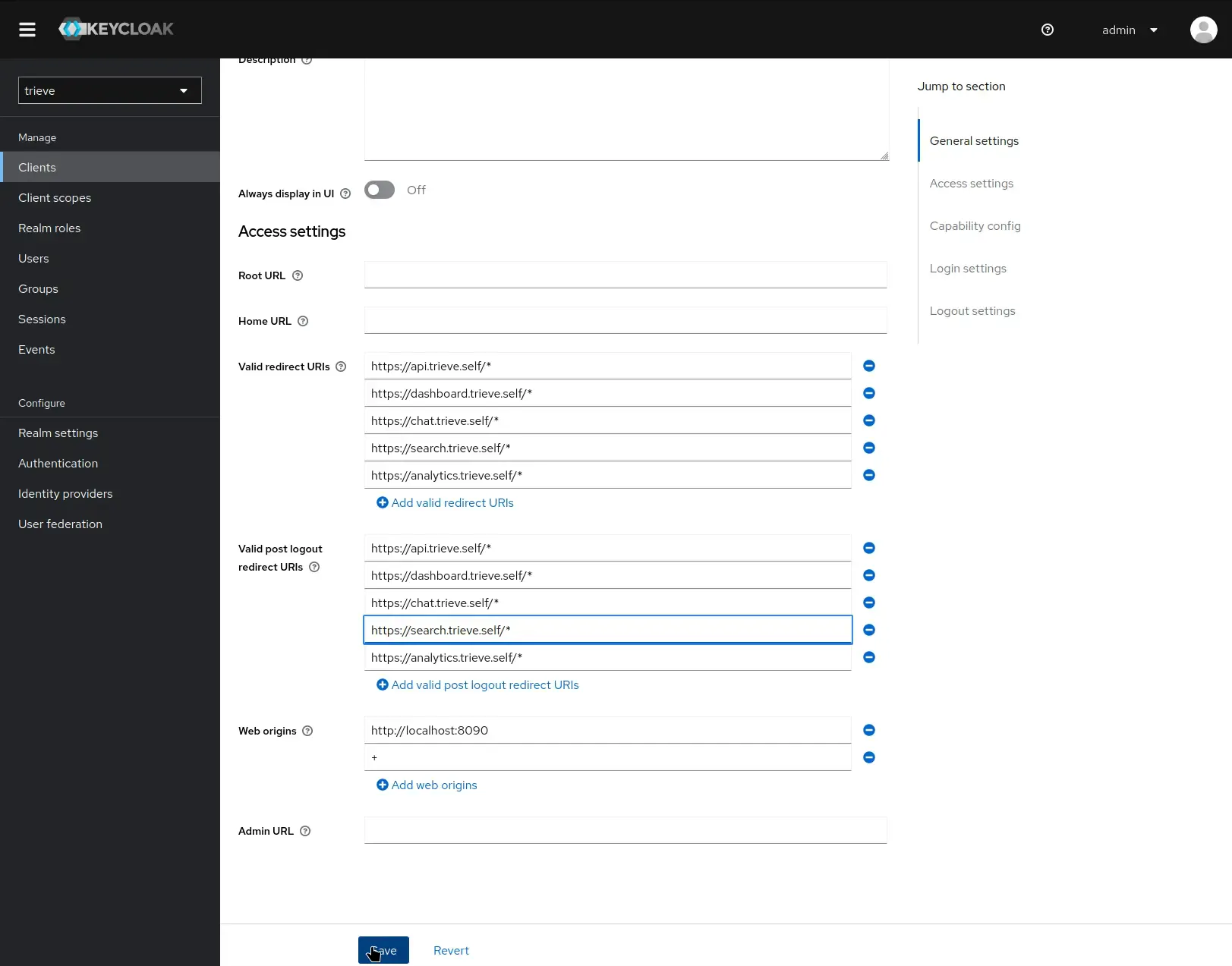
- Navigate to Clients → trieve → Settings
- Configure the Valid Redirect URIs and Valid Post Logout Redirect URIs (ensure it is https)
Verify Your Installation
Follow these steps to confirm your Trieve instance is working correctly:
Register Your First User
Navigate to dashboard.yourdomain.com in your browser. You’ll be prompted to register a new user account since this is a fresh installation.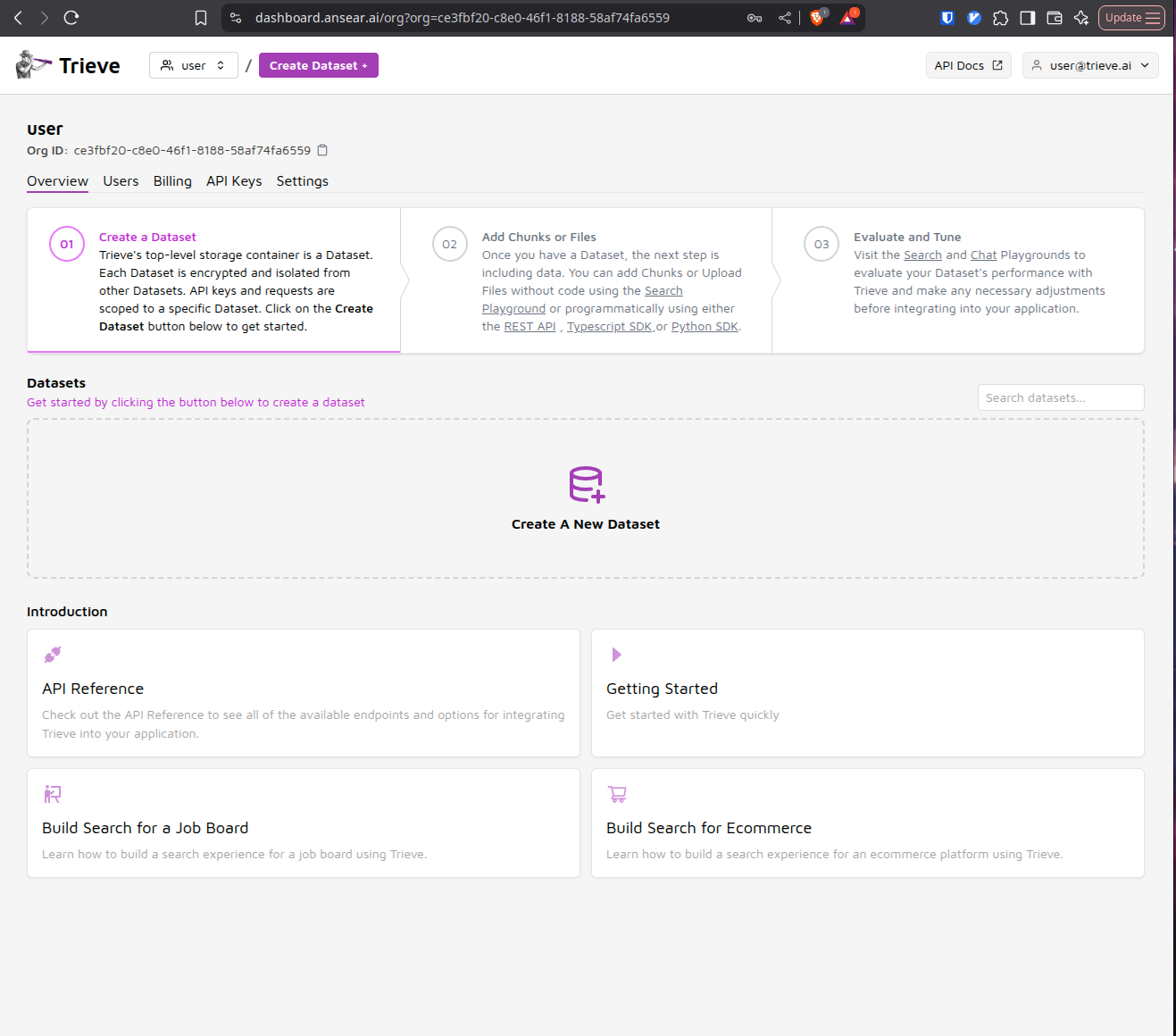
Create a Dataset and Add Sample Data
Once logged in, create your first dataset and populate it with some example data. This will help you test the core functionality of your Trieve instance.
Verify Data Processing
Check the admin event log to ensure that chunks are being created successfully from your uploaded data. This confirms that the ingestion pipeline is working properly.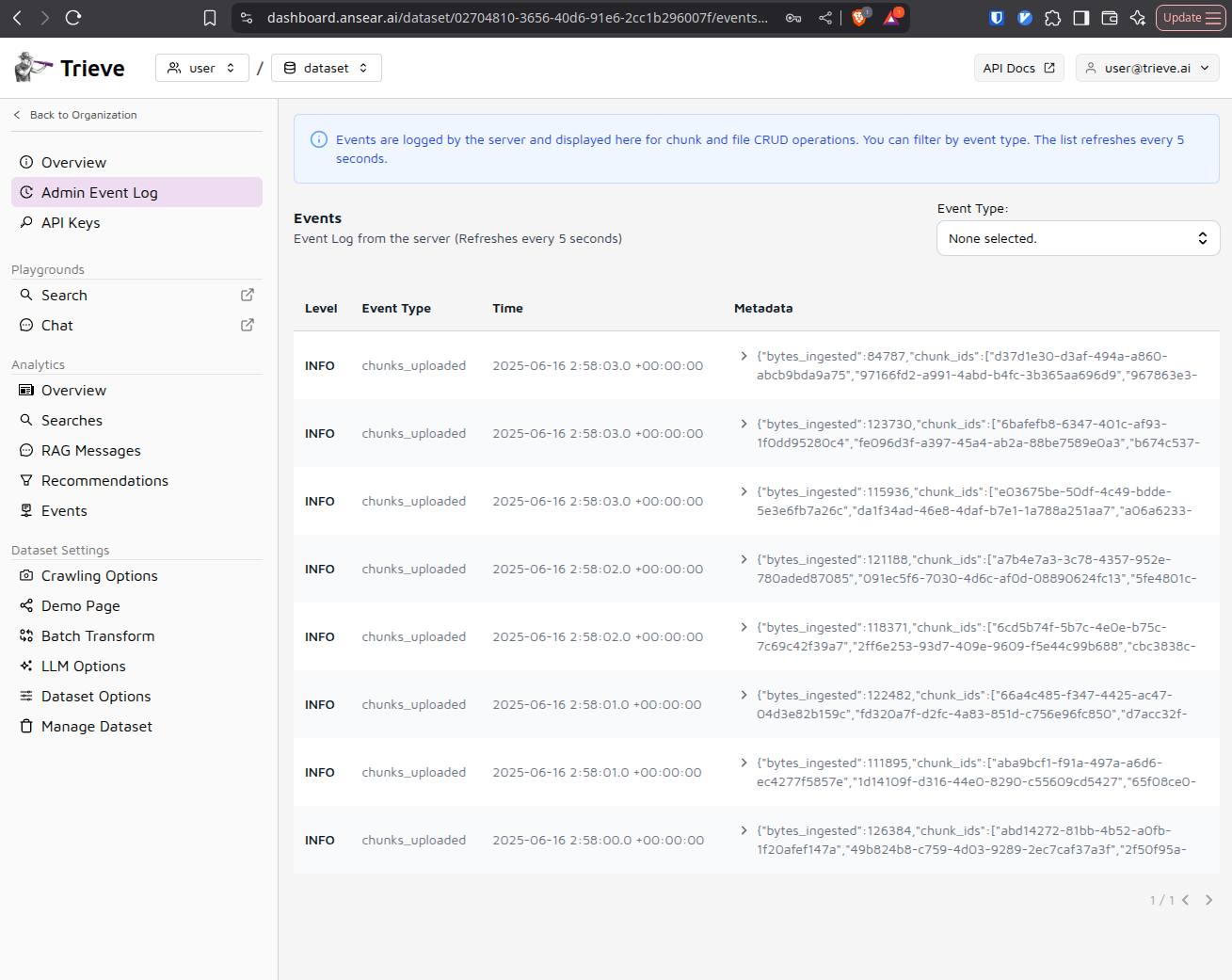
Test Search Functionality
Navigate to search.yourdomain.com and perform a test search query using the data you just uploaded. This verifies that the search engine is functioning correctly.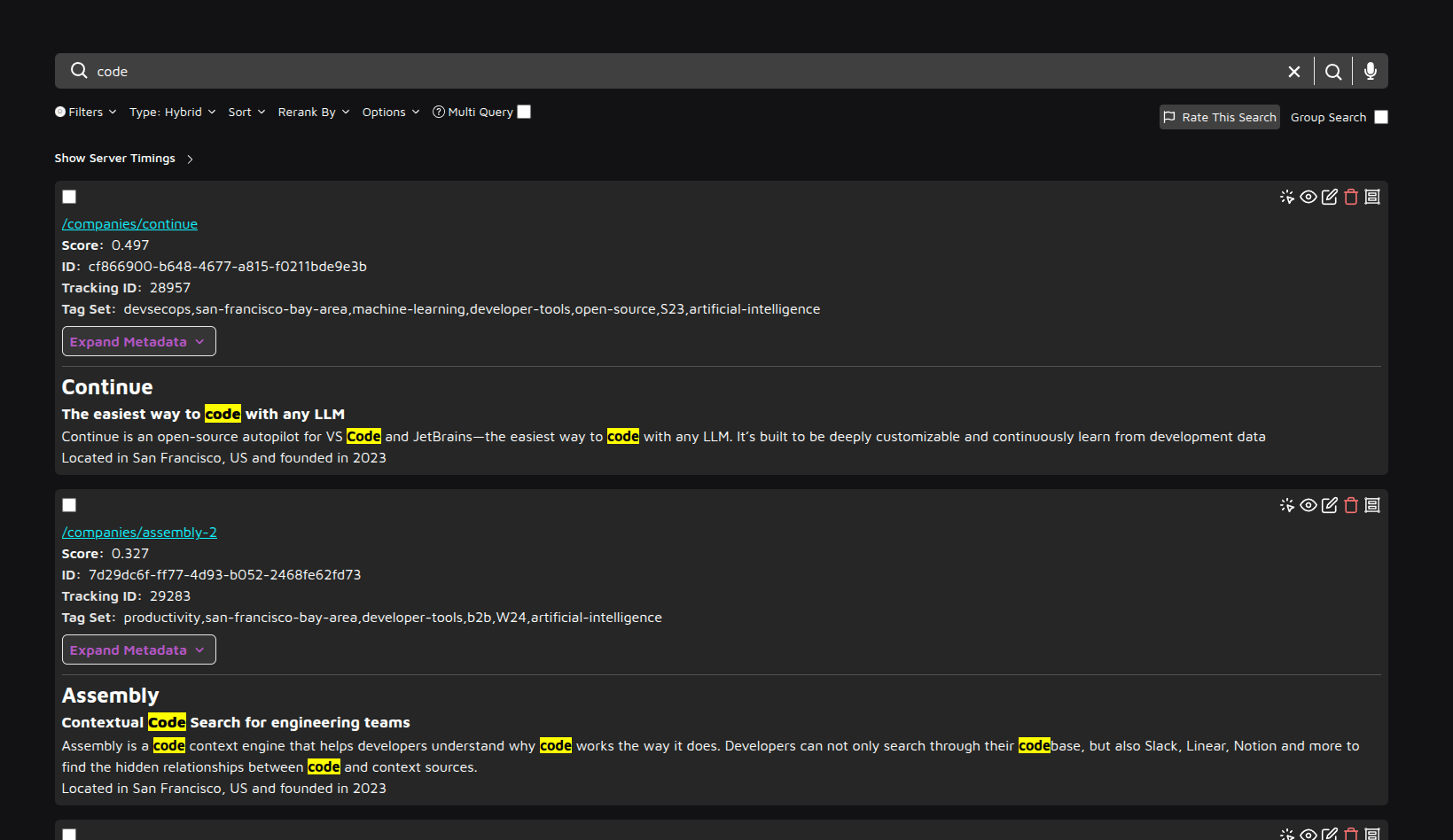
Review Search Analytics
Return to dashboard.yourdomain.com and examine your search analytics to confirm that queries are being tracked and analyzed properly.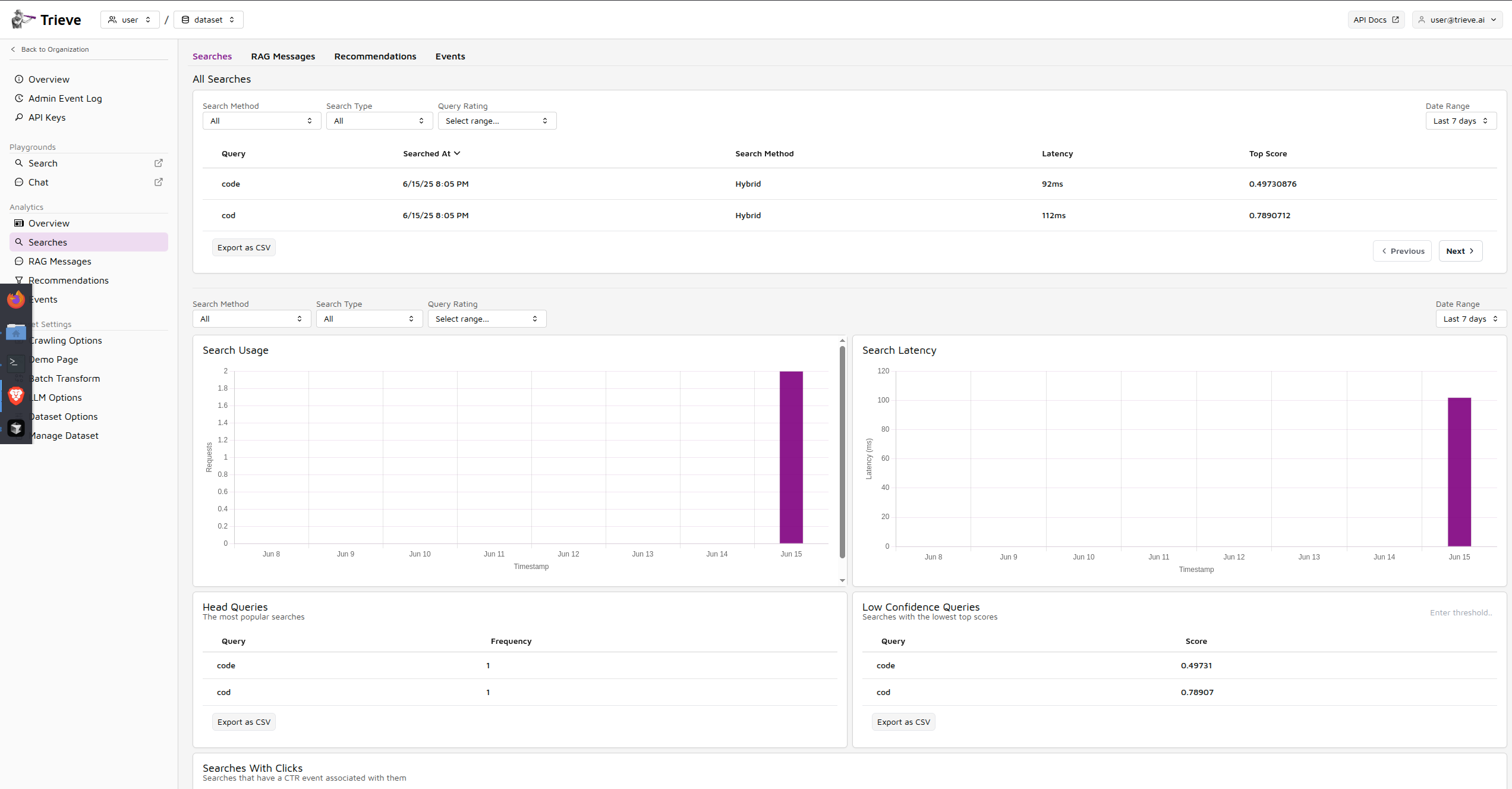
🚀 Congratulations! You’re all set!
You now have a fully functional Trieve instance running on AWS. Your self-hosted search infrastructure is ready to handle production workloads.
📚 Next Steps







